Clinical examination – Assessment
Veins
Veins
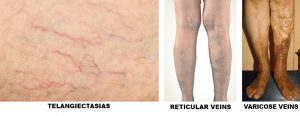
Telangiectasias:
Small, permanently dilated intradermal veins generally less than 1 mm in diameter that appear bluish distally (venous stasis) and purple proximally.
Reticular veins:
Bluish veins located within (intradermal) or immediately beneath the dermis that are dilated and tortuous or branched and measure between 1 and 3 mm in diameter (not to be confused with the highly visible normal veins in fair-skinned persons or athletes).
Varicose veins:
Superficial, usually sinuous subcutaneous veins (saphenous or non-saphenous) that have become dilated and are usually larger than 3 mm in diameter when the patient is in a standing position. Varicose veins are often the result of valve incompetency (reflux).